2020 University of Michigan Precision Health Symposium
Precision Health at the University of Michigan
The morning session is geared toward researchers, with speakers sharing best practices and the importance of engaging a community. The afternoon session will be appropriate for both research participants and researchers, as we focus on the impact of research on community. You may attend either or both sessions. All are welcome.
A virtual poster session, which begins at 11:10 a.m., will feature work by funded Precision Health investigators (we have funded $6 million in grants in our first two years!) and other invited researchers.
TO ATTEND A VIRTUAL POSTER DISCUSSION, click on the "chat" button during the poster session (11:10 a.m.-noon, September 23). Or click on the video button for the few posters featuring a pre-recorded video presentation.
More info: https://precisionhealth.umich.edu/news-events/2020-precision-health-symposium/
Genetic regulation of personalized opioid response in cerebral organoids
Stephanie Bielas1, Laura Scott2, John Barks3, Mats Ljungman4,5, Michael Boehnke2, Stephen CJ Parker1,6
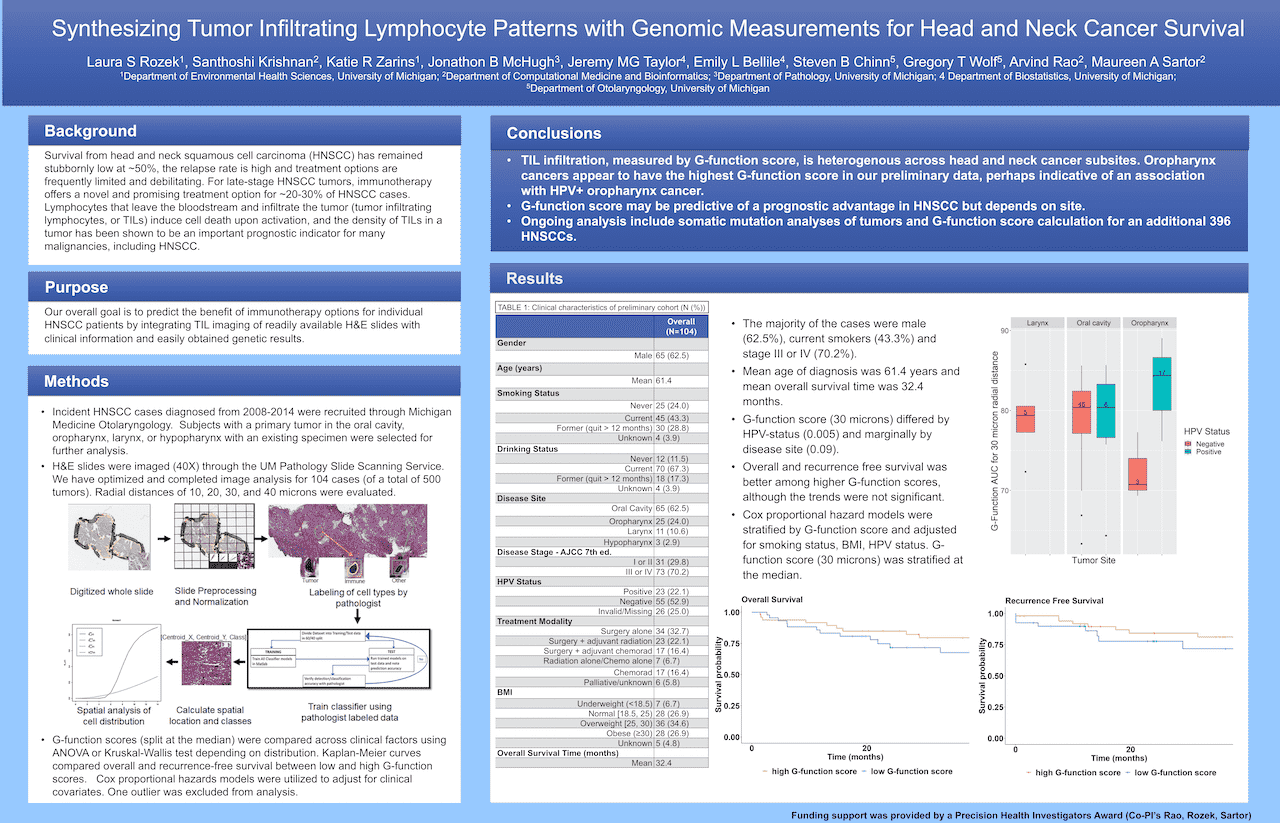
Synthesizing Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocyte Patterns with Genomic Measurements for Head and Neck Cancer Survival
Laura S Rozek1, Santhoshi Krishnan2, Katie R Zarins1, Jonathon B McHugh3, Jeremy MG Taylor4, Emily L Bellile4, Steven B Chinn5, Gregory T Wolf5, Arvind Rao2, Maureen A Sartor2
Revealing patient-specific intratumoral metabolic interactions by integrating multiomics data and flux analysis
Abhinav Achreja1,2,3, Ziwen Zhu1,2,3, Olamide Animasahun1,3,4, Anjali Mittal1,3,4, Noah Meurs1,2,3, Sarah Owen3,4, Sunitha Nagrath3,4,5, Deepak Nagrath1,2,3,4,5
A point-of-care microfluidic system for traumatic brain injury diagnosis and prognosis
Alyse D. Krausz, Sarah E. Mena, Martin P. de Beer, Frederick K. Korley, Mark A. Burns
Development and Validation of a Model to Predict Persistent Opioid Use Following Surgery
Singh, K., Vydiswararan, V.G., Murali, A. Strayhorn, A., Stevens, H., Brummett. C., Mellinger, J. A.; Winder, G. S., Bohnert, A.S.B, Fernandez, A.C.
Methods: This study included adults from the Michigan Genomics Initiative cohort undergoing surgery from January 5, 2015 to July 3, 2018, divided into a derivation cohort (surgery prior to July 4, 2017) and a validation cohort. Preoperative variables to predict persistent opioid use using logistic regression included demographics, comorbidities, surgical service, preoperative opioid fills (from Michigan’s Prescription Drug Monitoring Program), patient-reported measures (pain, mental health), and natural language processing-derived variables (risky alcohol and drug use). Persistent opioid use was defined as any perioperative opioid fill followed by any opioid fill 91-180 days postoperatively.
Results: The analysis included 19,352 eligible patients (derivation cohort - 14,671; validation cohort - 4,591) with a median age of 54 (IQR 40-64), 54% female, and 90% Caucasian. Overall, the model had an area under the receiver-operating-characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.80. Using standardized coefficients, the five most important variables were any preoperative opioid use, internal medicine-cardiology service, hydrocodone/acetaminophen use, acute care surgery, and chronic pain. Risky alcohol use was among the least important indicators.
Conclusions: A regression model derived from multiple data sources predicted persistent opioid use following surgery with more accuracy than other published models. These results highlight risk factors relevant for future prevention interventions.
Hardware Accelerated Seeding for Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis
Arun Subramaniyan, Jack Wadden, Kush Goliya, Nathan Ozog, Xiao Wu, Satish Narayanasamy, David Blaauw, Reetuparna Das
Software: https://github.com/arun-sub/bwa-mem2
Designing personalized combination therapies for tuberculosis using machine-learning and multi-scale modeling
Awanti Sambarey1, Joseph Cicchese2, Jennifer Linderman2, Denise Kirschner3, Zhenhua Yang4 and Sriram Chandrasekaran1*
Expressive Interviewing: A Conversational System for Coping with COVID-19
Charles Welch, Allison Lahnala, Verónica Pérez-Rosas, Siqi Shen, Sarah Seraj, Larry An, Kenneth Resnicow, James Pennebaker and Rada Mihalcea
An Alternative to the Sliding Window: Validating Dynamicity in Resting State fMRI with a Data-Driven Approach
Danai Koutra
Prediction of Coronary Artery Disease: From Statistical Models to Next-generation Clinical Application
Ida Surakka, Dakotah Feil, Brooke Wolford, Cristen Willer
Unsupervised Machine Learning Method for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Classification with Kidney Biopsies
Joonsang Lee1, Laura Mariani3, Salma Shaikhouni3, Joshua Bugbee2, Arvind Rao1 and Jeffrey Hodgin2
Methods: Thirty-eight trichrome digital slides from kidney biopsies were obtained from the C-PROBE Digital Pathology Image Repository at U-M. We performed unsupervised machine learning using a bag-of-words method to simplify representation used in natural language processing (NLP) using biopsy images tiled into 256x256 pixel patches for feature extraction. Features were clustered through K-means clustering and a histogram representation for each biopsy sample was created. We used a random forest model as a classifier to predict association with clinical patient outcomes such as eGFR.
Results: We estimated the optimal number of data cluster as 9 centroids (or phenotypes) represented as a cluster map. The out-of-back error from random forest is 0.23, sensitivity 0.74, and specificity 0.79. The area under ROC curve (AUC) is 0.77 and 95% confidence interval 0.613 – 0.927. F-score 0.76.
Conclusions: The results from our study showed that the visual dictionary (phenotypes) obtained from unsupervised machine learning could be novel features useful for discriminating levels of kidney function and could help in decision making during follow-up.
Defining Molecular Features of Treatment Response in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Tosoian, Jeffrey and Chinnaiyan, Arul
Methods: We identified 63 patients with oligometastatic PCa detected on imaging that underwent SLND at the San Raffaele Institute in Milan, Italy. Treatment response was defined as serum PSA <0.2 ng/ml following SLND, consistent with previous research. Positive lymph node tissue from responders and non-responders was submitted for DNA/RNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) and differential expression analysis. In-house sequencing pipelines and bioinformatic analyses were used to identify molecular markers of treatment response.
Results: Of 63 men undergoing SLND, 41 (65%) had a single positive site on pre-operative imaging. Post-operatively, 32 patients (51%) had PSA <0.2 ng/ml, and the remaining 31 patients (49%) were non-responders (i.e. PSA>0.2 ng/ml). Sequencing of responders and non-responders is underway to identify DNA- and RNA-based markers of response to SLND.
Conclusions: We hypothesize that potentially-curable oligometastatic PCa harbors molecular alterations distinct from aggressive, inevitably lethal disease. Identification of these alterations can be applied clinically to distinguish patients likely to benefit from metastasis-directed treatment from those better-suited for immediate systemic therapy, optimizing the treatment approach for each.
Virtual AppLication-supported ENvironment To INcrease Exercise (VALENTINE) during Cardiac Rehabilitation Study
Jessica R. Golbus MD, MS, Predrag Klasnja PhD, Bhramar Mukherjee PhD, Sachin Kheterpal MD, MBA, and Brahmajee K. Nallamothu MD, MPH
Methods: We are performing a prospective, randomized-controlled trial of 220 participants using a virtual study design. We will approach all low- and moderate-risk patients who enroll in CR at Michigan Medicine and who own a compatible smartphone. Participants will be randomized to a control or telehealth arm and followed for 6-months. Participants in both arms will receive usual care and will be provided with a smartwatch (an Apple Watch Series 4 or Fitbit Versa 2). Those in the telehealth arm will additionally receive the following interventions: (1) micro-randomized notifications which encourage activity and are tailored on 4 dimensions of context (weather, time of day, day of week, phase of behavior change); (2) weekly activity summaries via email tailored to phase of behavior change; and (3) activity tracking and goal setting through a mobile application. The primary outcome will be 6-minute walk distance assessed using a mobile application and smartwatch and, secondarily, step count.
Results: 5 participants have consented and enrolled virtually as part of a study pilot. The study will anticipate to launch on September 28, 2020.
Conclusions: Virtual consent and enrollment into a mobile device-facilitated telehealth program is feasible. Further study is needed to determine whether participation improves functional capacity after a cardiovascular event.
Assessing the feasibility of home-based balance training for older adults through automated evaluation of balance performance and personalized exercise progression
Christopher A. DiCesare1, Jeremiah Hauth1, Jamie Ferris1, Steven Teguhlaksana1, Wendy Carender1, Jenna Wiens2, Xun Huan1, Kathleen H. Sienko1
Cancer PRSweb – an Online Repository with Polygenic Risk Scores for Major Cancer Traits and Their Evaluation in Two Independent Biobanks
Lars G. Fritsche, Snehal Patil, Lauren J. Beesley, Peter VandeHaar, Maxwell Salvatore, Ying Ma, Robert B. Peng, Daniel Taliun, Xiang Zhou, Bhramar Mukherjee
Contact: Lars Fritsche (larsf@umich.edu)
Statistical inference for association studies using electronic health records: handling both selection bias and outcome misclassification
Lauren J. Beesley and Bhramar Mukherjee
Addressing misclassification and selection biases simultaneously is a more challenging problem than dealing with each on its own, and we propose several new strategies. For all methods proposed, we derive valid standard error estimators and provide software for implementation. We provide a new suite of statistical estimation and inference strategies for addressing misclassification and selection bias simultaneously that is tailored to problems arising in EHR data analysis. We apply these methods to data from The Michigan Genomics Initiative (MGI), a longitudinal EHR-linked biorepository.
Estimating Walking Speed in the Wild
1Loubna Baroudi, 1Mark Newman, 2Elizabeth Jackson, 1Kira Barton, 1Alex Shorter, and 1Stephen Cain
Psoriasis and Type 2 Diabetes Shared Genetic Loci through Trans-disease Meta-analysis
Matthew T Patrick, Philip E Stuart, Haihan Zhang, Qingyuan Zhao, Xianyong Yin, Kevin He, Xu-jie Zhou, Nehal N. Mehta, John J Voorhees, Michael Boehnke, Johann E Gudjonsson, Rajan P Nair, Samuel K. Handelman, James T Elder, Dajiang J Liu, Lam C Tsoi
Deep learning for Diagnosing Acute Dyspnea: Multi-modal and transfer learning approaches
Sarah Jabbour, Jenna Wiens, Ella Kazerooni, David Fouhey, Michael Sjoding
Development and Validation of Dynamic Multivariate Prediction Models of Sexual Function Recovery in Patients with Prostate Cancer Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy: Results from the MUSIC Statewide Collaborative
Nnenaya Agochukwu-Mmonu, Adharsh Murali, Daniela Wittmann, Brian Denton, Rodney L. Dunn, James Montie, James Peabody, David Miller, Karandeep Singh, for Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative
Short Tandem Repeats in Human Disease
Peter Todd, MD, PhD. Additional contributors/authors: Alex Weber, Torrin McDonald, Katelyn Green, Geena Skariah, Ryan E. Mills, Alan P Boyle
Using quantitative neuroimaging to enhance clinical prediction in Alzheimer’s dementia
Scott Peltier, Benjamin Hampstead, Luis Hernandez-Garcia, Jon-Fredrik Nielsen, Michelle Karker, Anish Lahiri, Navid Seraji-Bozorgzad, Doug Noll, Henry Paulson
External Validation of Postpartum Hemorrhage Prediction Models Using Electronic Health Record Data
Sean Meyer, MBA1; Alissa Carver, MD2; Hyeon Joo3; Tom Klumpner, MD*3; Karandeep Singh, MD, MMSc*4 *Co-senior authors
Methods: Using EHR data between 2/1/2019 and 5/11/2020, we identified delivery hospitalizations for women with an estimated gestational age of ≥ 22 weeks. After setting aside the most recent deliveries into a test set, we randomly divided the remaining into training (67%) and validation sets (33%). We mapped the 55 predictors used in the Venkatesh et al. model to EHR elements. We then fit logistic regression (LR), random forest (RF), and gradient-boosted machine (GBM) models (computer models) using the training and validation sets and compared their performance on the test set using an AUC.
Results: We identified 6,121 eligible hospital encounters, of which 1,354 were complicated by PPH. Of eligible encounters, 3,268 were in the training set, 816 in the validation set, and 2,037 in the test set. In the test set, AUCs for LR, RF, and GBM were .61, .60, and .62, respectively (only modestly predictive).
Conclusions: EHR predictors available at admission cannot reliably predict PPH. Updating model predictions during the hospital encounter may yield better performance.
RADIOHEAD: Radiogenomic Analysis Incorporating Tumor Heterogeneity in Imaging through Densities
Shariq Mohammed, Karthik Bharath, Sebastian Kurtek, Arvind Rao, and Veerabhadran Baladandayuthapani
Counseling-Style Reflection Generation Using Generative Pretrained Transformers with Augmented Context
Siqi Shen, Charles Welch, Rada Mihalcea, Verónica Pérez-Rosas
A Digital Protein Microarray for COVID-19 Cytokine Storm Monitoring
Yujing Song, Shiuan-Haur Su, Andrew Stephens, Yuxuan Ye, Tao Cai, Benjamin H. Singer, Katsuo Kurabayashi
Individualized Risk Assessment of Preoperative Opioid Use by Interpretable Neural Network Regression
Yuming Sun, Jian Kang, Chad Brummett, Yi Li
Targeting Branched Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Tumor Microenvironment
Ziwen Zhu, Abhinav Achreja, Noah Meurs, Olamide Animasahun, Sarah Owen, Anjali Mittal, Pooja Parikh, TingWen Lo, Janusz Franco-Barraza, Jiaqi Shi, Mara Sherman, Edna Cuikerman, Andrew Pickering, Anirban Maitra, Vaibhav Sahai, Meredith Morgan, Sunitha Nagrath, Thedore Lawrence, Deepak Nagrath